What is Automation?
Smart home automation involves using technology to automate and control various home functions, such as lighting, temperature, security, and appliances. These systems typically rely on interconnected devices that communicate with each other and can be controlled remotely via smartphones, tablets, or voice assistants.
Key Components
These components work together to create a connected and automated living environment.
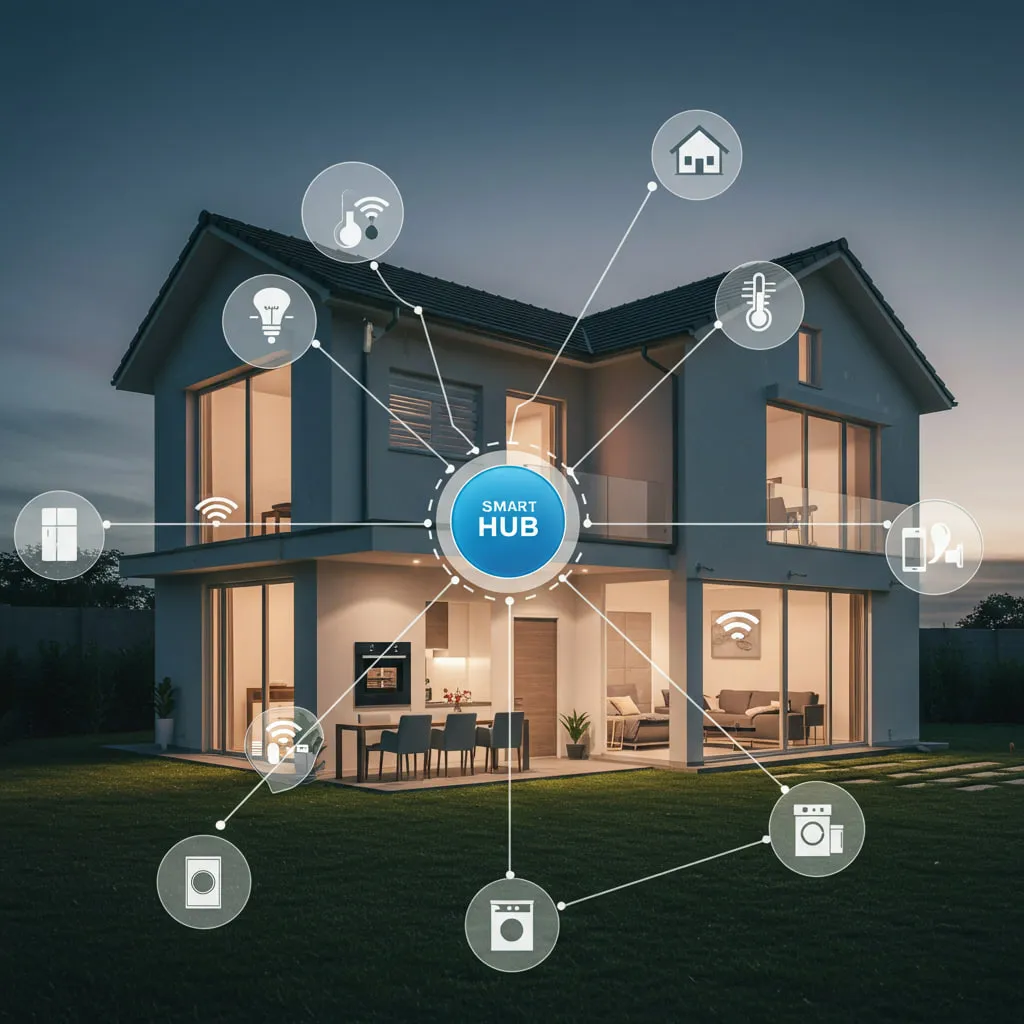

Smart Devices
These are the individual units that perform specific tasks, such as smart lights, thermostats, locks, appliances, and security cameras. They are the "actors" within the smart home ecosystem.
Hubs/Controllers
These act as the central command center, facilitating communication between different smart devices. They often manage communication protocols (like Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Wi-Fi) and allow for centralized control.
Network Connectivity
A stable and reliable internet connection is crucial for remote control, data transmission, and communication between devices and cloud services. Wi-Fi is the most common form of connectivity, but wired connections may also be used.
Software/Apps
These provide the user interface for controlling and managing smart home systems. They allow users to set schedules, create automation routines, and monitor device status.
Sensors
These devices monitor environmental changes, such as temperature, motion, or light levels. They provide the input that triggers automated actions.
Actuators
These are the devices, like motors or switches, that perform the physical actions dictated by the smart home system.
Voice Assistants
Platforms like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri enable hands-free voice control of smart home devices. They are a very common form of user interface.
Voice Control
Voice control simplifies smart home automation, offering a convenient, accessible, and intuitive way to manage connected devices and create personalized home experiences.

Hands-Free Convenience
Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri enable users to control devices with simple voice commands. This eliminates the need for physical interaction with switches, remotes, or smartphone apps.
Centralized Control
Voice assistants can act as a central hub, controlling a wide range of compatible smart home devices from various manufacturers. This simplifies the management of complex smart home ecosystems.
Simplified Automation
Voice commands can trigger complex automation routines and scenes. For example, "Good morning" can activate lights, adjust the thermostat, and start the coffee maker.
Accessibility
Voice control provides an accessible way for individuals with mobility impairments to interact with their homes. It offers a convenient alternative to traditional control methods.
Natural Language Interaction
Voice assistants use natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to user commands. This allows for more natural and conversational interactions.
Integration and Ecosystem
The value of voice control is heavily reliant on the size, and compatability, of the smart home ecosystem. The more devices that are compatable with a voice assistant, the more value that the voice assistant provides.
Ubiquitous Control
Voice assistants are becoming more common in many devices, such as phones, televisions, and speakers, allowing for control from almost anywhere in the home.
App Control
App control empowers users with comprehensive control over their smart home, offering remote access, customization, and real-time monitoring through intuitive mobile interfaces.

Centralized Device Management
Smartphone or tablet apps act as a central hub, allowing users to control and monitor various smart home devices from a single interface. This eliminates the need for multiple remotes or physical controls.
Remote Access and Control
Users can control their smart home devices from anywhere with an internet connection. This enables remote monitoring, adjustments, and automation, even when away from home.
Customization and Personalization
Apps provide granular control over device settings, allowing for personalized automation routines and scenes. Users can create customized schedules, triggers, and preferences.
Real-time Monitoring and Feedback
Apps provide real-time status updates and feedback from connected devices. This allows users to monitor energy consumption, security alerts, and device performance.
Integration and Interoperability
Smart home apps often facilitate integration between devices from different manufacturers. This enables seamless communication and automation across the smart home ecosystem.
User-Friendly Interface
Modern smart home apps are designed with user-friendly interfaces, making it easy to navigate and control devices. Visual representations and intuitive controls enhance the user experience.
Notification and Alert Systems
Apps provide notification and alert functionality, that notify the user of changes in the smart home enviroment. This is very useful for security, and safety applications.
Robots
Robots in smart home automation are moving beyond simple tasks, offering advanced automation, monitoring, and physical assistance, transforming homes into more intelligent and supportive environments.

Physical Assistance
Robots can perform physical tasks, such as cleaning (vacuuming, mopping), lawn maintenance, and even delivery within the home. This reduces the burden of household chores and enhances convenience.
Advanced Automation
Robots can integrate with other smart home devices to create complex automation routines. For example, a cleaning robot can coordinate with smart sensors to clean specific areas based on occupancy or mess detection.
Monitoring and Security
Robots equipped with cameras and sensors can act as mobile security patrols, monitoring the home for intrusions or anomalies. They can provide real-time video feeds and alerts to homeowners.
Personalized Interaction
Some robots can interact with occupants, providing information, entertainment, or assistance with daily tasks. They can learn user preferences and adapt their behavior accordingly.
Accessibility and Assistance
Robots can provide valuable assistance to individuals with mobility limitations or disabilities. They can perform tasks that are difficult or impossible for some individuals.
Developing Technology
Robotics in the home is a rapidly evolving field. New technologies are constantly being developed, that increase the functionality, and usefulness of these devices.
Integration Challenges
Integrating robots seamlessly into existing smart home ecosystems can be complex. Ensuring interoperability and compatibility is a key challenge.
Security Rules
Security rules in smart home automation provide a framework for proactive protection, automating responses to potential threats and empowering users to maintain a safe and secure connected environment.

Defining Threat Responses
Security rules dictate the system's actions when sensors detect anomalies, such as motion, door/window openings, or unusual device activity. These rules might trigger alarms, send notifications, activate cameras, or even initiate emergency services.
Automation Based on Security Events
Rules can automate responses to security events, like turning on lights when motion is detected at night or locking doors when an alarm is triggered. This proactive approach deters intruders and enhances overall security.
Customization and Personalization
Smart home systems allow for the creation of customized security rules tailored to individual needs and preferences. Users can define specific triggers, actions, and schedules based on their unique security concerns.
Real-time Alerts and Notifications
Security rules often include real-time alerts and notifications sent to smartphones or other devices. This ensures that users are immediately informed of potential security breaches, enabling prompt action.
Integration with Security Services
Advanced security rules can integrate with professional security services, such as armed response or monitoring companies. This enables rapid intervention in case of a confirmed security threat.
Balancing Security and Convenience
Effective security rules strike a balance between robust protection and user convenience. They minimize false alarms while ensuring prompt responses to genuine security threats.
Cybersecurity Rules
Security rules also apply to network security. Rules can be put in place that block outside network access to specific IOT devices, or that alert the user of unusual network traffic.
Efficiency Rules
Efficiency rules in smart home automation promote sustainable living by automating resource management, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy consumption.
Automated Energy Management
Efficiency rules automate energy-consuming devices like thermostats, lighting, and appliances based on usage patterns, occupancy, and environmental factors. This minimizes energy waste and lowers utility bills.
Optimized Resource Consumption
Rules can control devices like irrigation systems based on weather conditions or soil moisture, conserving water. They can also manage appliance usage during off-peak hours to reduce energy costs.
Occupancy-Based Control
Efficiency rules can leverage occupancy sensors to automatically turn off lights, adjust thermostats, or power down devices when rooms are unoccupied. This ensures that resources are only used when needed.
Scheduled Automation
Rules can schedule device operation based on time of day, day of week, or other time-based parameters. This allows for automated energy savings during periods of low usage.
Integration with Environmental Sensors
Efficiency rules can integrate with environmental sensors, such as temperature, humidity, and light sensors, to optimize device operation based on real-time conditions. For example, lights can dim automatically when natural light is sufficient.
Feedback and Monitoring
Smart home systems can provide feedback and monitoring data on energy consumption and resource usage. This allows users to track their efficiency and make adjustments as needed.
Device coordination
Efficiency rules can coordinate the actions of multiple devices. For example, when the sun is providing enough light, the blinds can close, and the air conditioning can turn on, to keep the house cool.
Convenience
Convenience in smart home automation focuses on simplifying daily life, enhancing comfort, and providing greater control over the home environment through automation and seamless integration.

Automation of Routine Tasks
Smart home systems automate repetitive tasks, such as turning on lights, adjusting thermostats, or starting appliances. This frees up time and mental energy for more important activities.
Remote Control and Access
Users can control and monitor their homes from anywhere with a smartphone or voice assistant. This provides flexibility and peace of mind, even when away from home.
Personalized Environments
Smart home systems allow for the creation of personalized environments tailored to individual preferences. This includes customized lighting scenes, temperature settings, and entertainment options.
Simplified Device Management
Centralized control through apps or voice assistants eliminates the need for multiple remotes or physical controls. This streamlines device management and simplifies interactions.
Seamless Integration
Smart home systems seamlessly integrate various devices and services, creating a cohesive and automated living experience. This allows for smooth transitions between different activities and environments.
Increased Accessibility
Voice control and automated features enhance accessibility for individuals with mobility limitations. This promotes independence and improves quality of life.
Contextual Awareness
Smart home systems can use sensors, and user habits, to react to the context of the enviroment. For example, if it is raining, close the windows, and turn on the inside lights.
